Prominent Scientists Declare “All Non Human Animals… Are Conscious Beings.” The Dalai Lama Protests Chicken Slaughter. An Orangutan Won Non-Human Rights Over Zoo Keeper. What Do the Teachers Say About Non-Human Compassion?
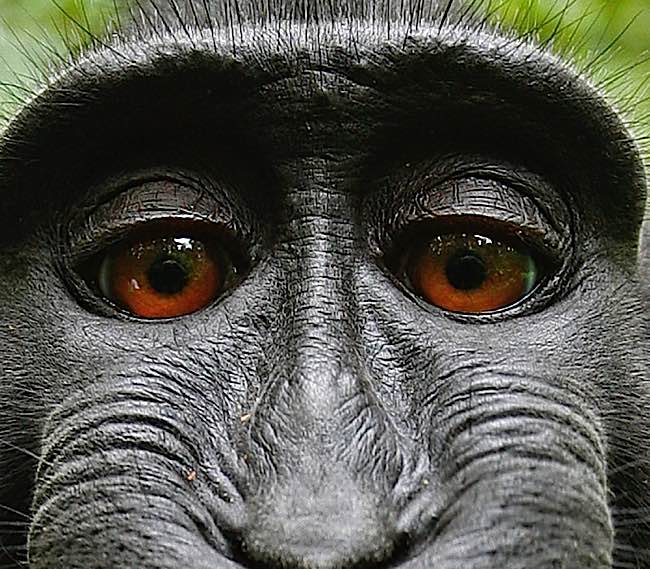
A prominent international group of cognitive neuroscientists and other experts made a strong declaration, endorsed by Stephen Hawking, affirming that all “nonhuman animals… including octopuses” are sentient and feel emotions such as fear and happiness. In Argentina, an orangutan won non-human rights against his zoo-keeper. Recently, in the news, a monkey won the rights to a selfie photo over the owner of the camera. [See photo.]
The advance in non-human rights begs the question — from a Buddhist perspective, where we promise to liberate all sentient beings, or not to kill — just who do we include? If our definition includes all beings down to insects and octopuses, how do we reconcile our dependence on “lower” beings for survival?
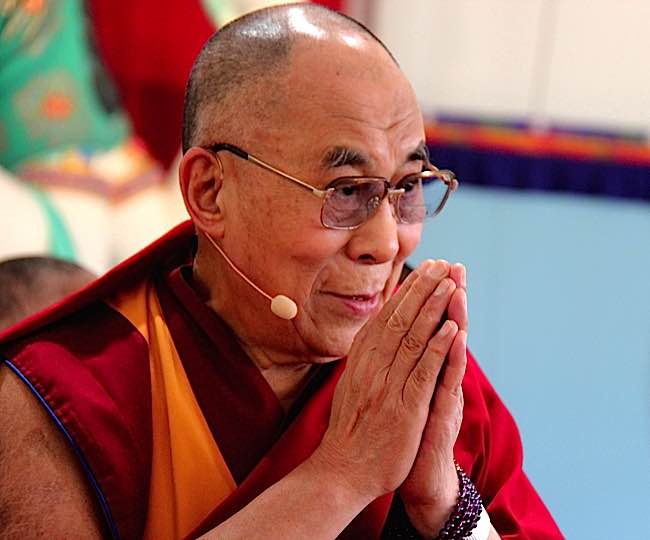
Increasingly, teachers are speaking out on non-human sentience and unnecessary suffering for these beings. When the Dalai Lama famously protested “cruelty to chickens” in 2012, it was inspired by an abundance of compassion (see “Dalai Lama and Chickens” below). How does the “Cambridge Declaration” from an international group of prominent scientists, stating that even octopuses feel emotions, change our view? More importantly, what do our teacher’s say? To help provide insight, we collected teachings from the Buddha, the Dalai Lama, Bikkhu Bodhi, Thich Nhat Hanh, Zasep Tulku Rinpoche, Karma Lekshe Tsomo, Lama Zopa Rinpoche, Kyabje Chatral Sangye Rinpoche, Geshe Thubten Soepa, and, of course, Stephen Hawking and the Cambridge Scientists.
Buddha: First Precept “Abstain from Taking Life”
Mahayana Buddhists, who promise to Liberate All Sentient Beings” are often vegetarian out of compassion for the suffering of non-human beings—to fulfill Bodhisattva vow and the first precept of Buddha not to kill. For others, it is often convenient to avoid the topic, since we are often brought up culturally to accept the necessary killing of animals for survival.

The Buddha’s first precept in Pali reads: “Panatipata verami sikkhapadam samadiyami” which translates more-or-less as: “I undertake the training rule to abstain from taking life.” For many, this meant human life. For others, particularly Zen Buddhists, it meant any breathing creature.

Cambridge Declaration: “Human’s not unique in possessing … consciousness.”
“Convergent evidence indicates that non-human animals have the neuroanatomical, neurochemical, and neurophysiological substrates of conscious states along with the capacity to exhibit intentional behaviors. Consequently, the weight of evidence indicates that humans are not unique in possessing the neurological substrates that generate consciousness. Nonhuman animals, including all mammals and birds, and many other creatures, including octopuses, also possess these neurological substrates.” — The Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness (See full text of official declaration at bottom of this feature.)
The scientists demonstrated that emotions and decision-making develop in all life forms down to cephalopod mollusks. Even Steven Hawking and other giants endorsed the declaration, titled “The Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness.” Issued by a prominent group of neurophysiologists, neuroanatomists, cognitive neuroscientists, neuropharmacologists and computational neuroscientists — this statement leaves little wiggle room for diminishing levels of compassion for “lower” life forms. [To read the full declaration, the PDF is available for download here>>] (View the video from Stephen Hawking on the sentience of lower animals, embedded below)
Stephen Hawking and Non-Human Consciousness
On the heels of this declaration, an orangutan in an Argentinian zoo won non-human personhood rights in a fight to determine if it had been unlawfully deprived of it’s freedom. Also, the credit for the “selfie” at the top of our feature is under legal review to determine whether the monkey or the owner of the camera deserved the credit. [7]
In another related story, Professor Marc Bekoff wrote in Psychology Today: “We know, for example, that mice, rats, and chickens display empathy…” Which brings us to chickens and the Dalai Lama.

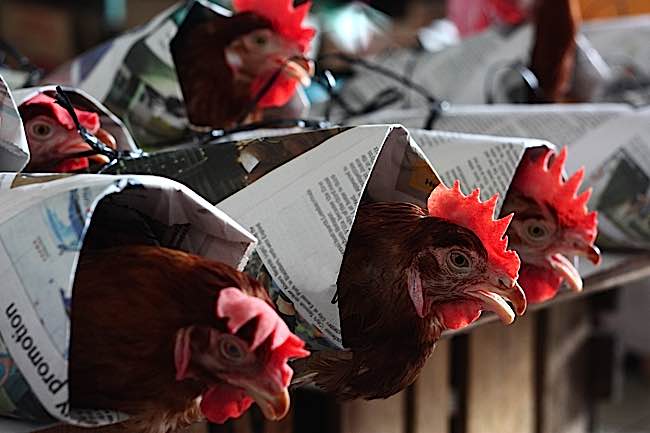
Dalai Lama’s “Cruelty to Chickens” Letter
In 2012, Buddha Weekly reported on the Dalai Lama’s protest letter, in which he wrote to KFC: “I have been particularly concerned with the suffering of chickens for many years.” At the time KFC slaughtered 850 million chickens each year (as of 2010). The Dalai Lama wrote to KFC, asking them to abandon their plan to open restaurants in Tibet “because your corporation’s support for cruelty and mass slaughter.” [1]
At the time, PETA proclaimed that chickens “feel pain and have distinct personalities and intelligence,” which was largely scoffed at publically. This later finding of the scientists at Cambridge University would seem to support both PETA and the rationale for the Dalai Lama’s protest.

Killing is prohibited in Buddhism — clearly one of the main precepts — but often this is simply interpreted to mean “human” killing — on the basis that lower animals are not sentient. Even if killing of “lower animals” is necessary for survival, the doctrine of Metta prohibits Buddhists from causing suffering.
The Dalai Lama explained how he had become a vegetarian after witnessing the slaughter of a chicken. ” It was the death of a chicken that finally strengthened my resolve to become vegetarian. In 1965, I was staying at the Government Guest House in south India. My room looked directly on to the kitchens opposite. One day I chanced to see the slaughter of a chicken, which made me decide to become a vegetarian.”
He also explained why he particularly focused on chickens. “Tibetans are not, as a rule, vegetarians, because in Tibet vegetables are scarce and meat forms a large part of the staple diet. However, it is considered more ethical to eat the meat of larger animals such as yaks, than small ones, because fewer animals would have to be killed.”
Even the Buddha was not a strict vegetarian. He ate what his sponsors provided in his bowl, including meat. It was, according to tradition, tainted meat that led to his death and paranirvana.

Bikkhu Bodhi: Sentient Being — “Any Being with Breath”
Theravadan Pali Canon tends to support the notion of all life as sentient. The well-known teacher Bikkhu Bodhi explains “pana” (from the First Precept in Pali ‘”pana” means “breathing, or any living being that has breath and consciousness.”) The Venerable teacher explains that this includes all animal life, including insects, but not plant life. The word “anipata” means to “strike down, and includes both killing and injuring or torturing. [8] Clearly, it is critical to avoid taking the life of “any being with breath.”
A key element in motivation. Accidentally stepping on an insect or running over an animal on the road would not generally be in conflict with the First Precept.

Zasep Tulku Rinpoche: “We must not hurt other people and animals.”
Venerable Zasep Rinpoche, spiritual director of Gaden for the West and Gaden Choling, emphasizes “right livelihood” to his students. He is unequivocal in his advice on the equal weight of importance between humans and non-humans. Rinpoche wrote in his Guidelines: “Right livelihood is one of the aspects of the eightfold noble path; it is an important Buddhist principle that we as Dharma practitioners practise right livelihood. We must not hurt other people and animals, and we must make the best use of the earth’s resources, in ways that do not do social and environmental damage.”

Karma Lekshe Tsomo: “Examine … Motivation”
Karma Tsomo, a professor of theology and a Tibetan nun said: “When making moral choices, individuals are advised to examine their motivation–whether aversion, attachment, ignorance, wisdom, or compassion–and to weigh the consequences of their actions in light of the Buddha’s teachings.” [8]
The same criterion would be important in issues of “self defense” including defense of one’s country in a time of war. According to Barbara O’Brien, “some 3,000 Buddhists” serve “in the U.S. armed forces, including some Buddhist chaplains. Buddhism does not demand pacificism.” Again, however motivation is key, in this case the “motivation” of the country sponsoring the soldier. Is the action that led to killing due to the negative motivation of the country, such as greed, attachment, hatred or ignorance? [8]

Thich Nhat Hanh: “No Killing Can be Justified”
The famous Zen monk and pacifist, who was once nominated for a Nobel Peace Prize is unequivicol in his view of the first precept against killing: “We cannot support any act of killing; no killing can be justified. But not to kill is not enough. We must also learn ways to prevent others from killing. We cannot say, “I am not responsible. They did it. My hands are clean.” If you were in Germany during the time of the Nazis, you could not say, “They did it. I did not.” If, during the Gulf War, you did not say or do anything to try to stop the killing, you were not practicing this precept. Even if what you said or did failed to stop the war, what is important is that you tried, using your insight and compassion.” [9]
Not only is the venerable teacher a well-known pacifist activist, he is also vegetarian. “Even if we take pride in being vegetarian, for example, we have to acknowledge that the water in which we boil our vegetables contains many tiny microorganisms. We cannot be completely nonviolent, but by being vegetarian, we are going in the direction of nonviolence. If we want to head north, we can use the North Star to guide us, but it is impossible to arrive at the North Star. Our effort is only to proceed in that direction.”

Lama Zopa Rinpoche: “Animals Experience Unbelievable Suffering”
The most Venerable Vajrayana teacher Lama Zopa Rinpoche replied to a student on the subject of vegetarianism: ” As there are more and more people becoming vegetarian, that means less and less animals will be killed. So it is very important. In the world people eat meat mainly because of habit; so many people have not thought that the animals experience unbelievable suffering.” [4]
He later described how he saw a cow struggling to not go down a ramp to slaughter: ” A man was pulling him down from the platform, but the cow didn’t want to go down. So I thought, I can’t stop the animal suffering, but what I can do as I go around the world to teach, even if it is on sutra and tantra, I will announce or request if people can become vegetarian. That is something I can do.”

Bodhisattva Vow: “Liberate All Sentient Beings”
In Mahayana Buddhism, often the definition of “sentient beings” is any being who is capable of experiencing Dukkha (suffering.) According to the Cambridge scientists, this is all beings down to and including octopuses.
In sutra, sentient beings are described as all inhabitants of the three realms of samsara within the six classes of beings. Included in the six classes are animals, fish, insects — any creature with mind. Particularly as relates to the Tathagatagarbha doctrine, all these creatures have inherent Buddha Nature, “the intrinsic potential to transcend the conditions of Samsara and attain Enlightenment.” [3]

Kyabje Chatral Sangye Dorje Rinpoche: “Meat, the sinful food.”
The great Kyabje Chatral Sangye Dorje Rinpoche, a highly realized Dzogchen yogi, was a vocal opponent of meat for all of his long life, from 1913-2015. “If you take meat, it goes against the vows one takes in seeking refuge in the Buddha Dharma and Sangha. Because when you take meat you have to take a being’s life.”
In Chapter 2 of “Compassionate Action” he wrote: Meat, the sinful food, is not permitted according to the three vows: the vows of individual liberation, the Bodhisattva vows and the tantric vows.” [6]
On the other hand, many Buddhists are not vegetarians. Buddha Himself taught monks to eat whatever was placed in their bowl, including meat, unless they knew the animal was slaughtered for the monks. (See “First Precept: Killing versus Eating below).

Buddha Taught Loving Kindness — but Not Just for Humans?
Without question, practicing Buddhists practice compassion and loving kindness — metta — for sentient beings. The doctrine of “karuna” or “active sympathy” and willingness “to bear the pain of others” is not debatable — at least not in Mahayana schools. Even if we interpret “compassion” to be a skillful method used by the Buddha to demonstrate the mistaken idea of “independent me” and “independent you” — there can be no doubt that kindness for sentient beings is not optional.
There is no question that the Buddha taught loving-kindness for all sentient beings not just humans. Why is this critical? Because Buddha also taught the doctrine of rebirth — that we can be reborn as insects, lower animals, and other forms of life. Compassion for all beings, down to crawling insects, is not implicit, it appears to be explicitly recommended. This does not mean Buddhists must be vegetarians, but at least that we must feel sympathy for the suffering of all creatures.
How Equally Do We Practice Compassion?
These findings of neuroscientists, when positioned against the Buddhist Dharma, beg the question: how equally do we practice compassion? We might feel more compassion, for example, for our beloved canine or feline. We might feel “sorry” for the beautiful deer lying by the side of the road, struck by a car. We might, like the Dalai Lama, feel sorry for the chicken, especially if we see a picture of a beautiful new-born chick. Do we then feel similar levels of sympathy for the insects splattered on our windshield, or the “less attractive” creatures such as spiders and venomous snakes?
Whether we accept the notion that we might be reborn as a future splattered insect, there can be no doubt that we are taught that our mission is to “free all sentient beings from Samsara.” How much worse is it when we, ourselves, create the causes of suffering?
First Precept: Killing versus Eating? They’re Different Right?
The first precept Buddha taught was not to kill. However, certainly in Pali cannon, this is usually not interpreted to prohibit the eating of meat — only the killing of the animal or the sponsoring of the killing. Mahayana sutras, tend to strongly advocate vegetarianism, particularly the Lankavatara Sutra. [2] In the Jivaka Sutta, Buddha probited the monks from consumption of the flesh of any animal that was seen or suspected to have been killed for the benefit of the monks. Generally, monks were expected to accept and respect all alms provided in their bowls, including meat, without discrimination.
Clearly, this later became an issue when monks formed communities and monasteries, where it became more difficult to argue that the animal was not killed specifically for their benefit. As devout Buddhists, the argument, therefore, comes down to whether we believe the meat on the supermarket shelf was killed for our benefit. If we believe we are not encouraging the killing, or supporting cruelty, then it would not be considered a conflict with the first precept. If we believed that by buying the meat we are supporting the slaughter of animals, we would be in conflict. Ultimately, that’s a personal choice. While meat might be debatable, what is clearly not permitted, according to this precept, is the deliberate slaughter of a sentient being, including chickens.

Geshe Thubten Soepa: “Meat Not Allowed”
In a question and answer series about vegetarianism with Geshe Thubten Soepa, a FPMT-registered teacher, he answers: “In the Mahayana teachings the Buddha forbade eating meat altogether. In many different sutras (the Lankarawatara Sutra, the Great Sutra of Nirvana in the Angulimala Sutra, the Sutra on the Ability of the Elephant, the Sutra of the Great Cloud), it is taught that if one is trying to live with great compassion, then eating meat is not allowed. This is because one has to see all sentient beings as our mother, brother, son, etc. Also in the Angulimala Sutra, Manjushri asked the Buddha, ‘‘Why do you not eat meat?’’ He replied that he saw all beings as having buddha-nature and that was his reason for not eating meat. Therefore, if you practice Mahayana and eat meat, it is a contradiction.” [5]

The Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness*
Here is the full text of the Declaration on Consciousness:
On this day of July 7, 2012, a prominent international group of cognitive neuroscientists, neuropharmacologists, neurophysiologists, neuroanatomists and computational neuroscientists gathered at The University of Cambridge to reassess the neurobiological substrates of conscious experience and related behaviors in human and non-human animals. While comparative research on this topic is naturally hampered by the inability of non-human animals, and often humans, to clearly and readily communicate about their internal states, the following observations can be stated unequivocally:
- The field of Consciousness research is rapidly evolving. Abundant new techniques and strategies for human and non-human animal research have been developed. Consequently, more data is becoming readily available, and this calls for a periodic reevaluation of previously held preconceptions in this field. Studies of non-human animals have shown that homologous brain circuits correlated with conscious experience and perception can be selectively facilitated and disrupted to assess whether they are in fact necessary for those experiences. Moreover, in humans, new non-invasive techniques are readily available to survey the correlates of consciousness.
- The neural substrates of emotions do not appear to be confined to cortical structures. In fact, subcortical neural networks aroused during affective states in humans are also critically important for generating emotional behaviors in animals. Artificial arousal of the same brain regions generates corresponding behavior and feeling states in both humans and non-human animals. Wherever in the brain one evokes instinctual emotional behaviors in non-human animals, many of the ensuing behaviors are consistent with experienced feeling states, including those internal states that are rewarding and punishing. Deep brain stimulation of these systems in humans can also generate similar affective states. Systems associated with affect are concentrated in subcortical regions where neural homologies abound. Young human and nonhuman animals without neocortices retain these brain-mind functions. Furthermore, neural circuits supporting behavioral/electrophysiological states of attentiveness, sleep and decision making appear to have arisen in evolution as early as the invertebrate radiation, being evident in insects and cephalopod mollusks (e.g., octopus).
- Birds appear to offer, in their behavior, neurophysiology, and neuroanatomy a striking case of parallel evolution of consciousness. Evidence of near human-like levels of consciousness has been most dramatically observed in African grey parrots. Mammalian and avian emotional networks and cognitive microcircuitries appear to be far more homologous than previously thought. Moreover, certain species of birds have been found to exhibit neural sleep patterns similar to those of mammals, including REM sleep and, as was demonstrated in zebra finches, neurophysiological patterns, previously thought to require a mammalian neocortex. Magpies in particular have been shown to exhibit striking similarities to humans, great apes, dolphins, and elephants in studies of mirror self-recognition.
- In humans, the effect of certain hallucinogens appears to be associated with a disruption in cortical feedforward and feedback processing. Pharmacological interventions in non-human animals with compounds known to affect conscious behavior in humans can lead to similar perturbations in behavior in non-human animals. In humans, there is evidence to suggest that awareness is correlated with cortical activity, which does not exclude possible contributions by subcortical or early cortical processing, as in visual awareness. Evidence that human and nonhuman animal emotional feelings arise from homologous subcortical brain networks provide compelling evidence for evolutionarily shared primal affective qualia.
We declare the following: “The absence of a neocortex does not appear to preclude an organism from experiencing affective states. Convergent evidence indicates that non-human animals have the neuroanatomical, neurochemical, and neurophysiological substrates of conscious states along with the capacity to exhibit intentional behaviors. Consequently, the weight of evidence indicates that humans are not unique in possessing the neurological substrates that generate consciousness. Nonhuman animals, including all mammals and birds, and many other creatures, including octopuses, also possess these neurological substrates.”
* The Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness was written by Philip Low and edited by Jaak Panksepp, Diana Reiss, David Edelman, Bruno Van Swinderen, Philip Low and Christof Koch. The Declaration was publicly proclaimed in Cambridge, UK, on July 7, 2012, at the Francis Crick Memorial Conference on Consciousness in Human and non-Human Animals, at Churchill College, University of Cambridge, by Low, Edelman and Koch. The Declaration was signed by the conference participants that very evening, in the presence of Stephen Hawking, in the Balfour Room at the Hotel du Vin in Cambridge, UK. The signing ceremony was memorialized by CBS 60 Minutes. [10]
NOTES
[1] “Cruelty to Chickens Protest: Dalai Lama“, Buddha Weekly
[2] “Buddhism and Vegetarianism“, UrbanDharma.org
[3] “Sentient Beings”
[4] “Inspired to Become a Vegetarian” Lama Zopa Rinpoche
[5] “Nine Questions About Vegetarianism” with Geshe Thubten Soepa, FPMT
[6] “Kyabje Chatral Sangye Dorje Rinpoche”
[7] “Orangutan in Argentina Wins Non Human Person Rights“, Raw Science
[8] “The First Buddhist Precept, To Abstain from Taking Life,” by Barbara O’Brien
[9] “The First Precept: Reverence for Life” by Thich Nhat Hanh
Latest Features
Please support the "Spread the Dharma" mission as one of our heroic Dharma Supporting Members, or with a one-time donation.
Please Help Support the “Spread the Dharma” Mission!

Be a part of the noble mission as a supporting member or a patron, or a volunteer contributor of content.
The power of Dharma to help sentient beings, in part, lies in ensuring access to Buddha’s precious Dharma — the mission of Buddha Weekly. We can’t do it without you!
A non-profit association since 2007, Buddha Weekly published many feature articles, videos, and, podcasts. Please consider supporting the mission to preserve and “Spread the Dharma." Your support as either a patron or a supporting member helps defray the high costs of producing quality Dharma content. Thank you! Learn more here, or become one of our super karma heroes on Patreon.
Lee Kane
Author | Buddha Weekly
Lee Kane is the editor of Buddha Weekly, since 2007. His main focuses as a writer are mindfulness techniques, meditation, Dharma and Sutra commentaries, Buddhist practices, international perspectives and traditions, Vajrayana, Mahayana, Zen. He also covers various events.
Lee also contributes as a writer to various other online magazines and blogs.